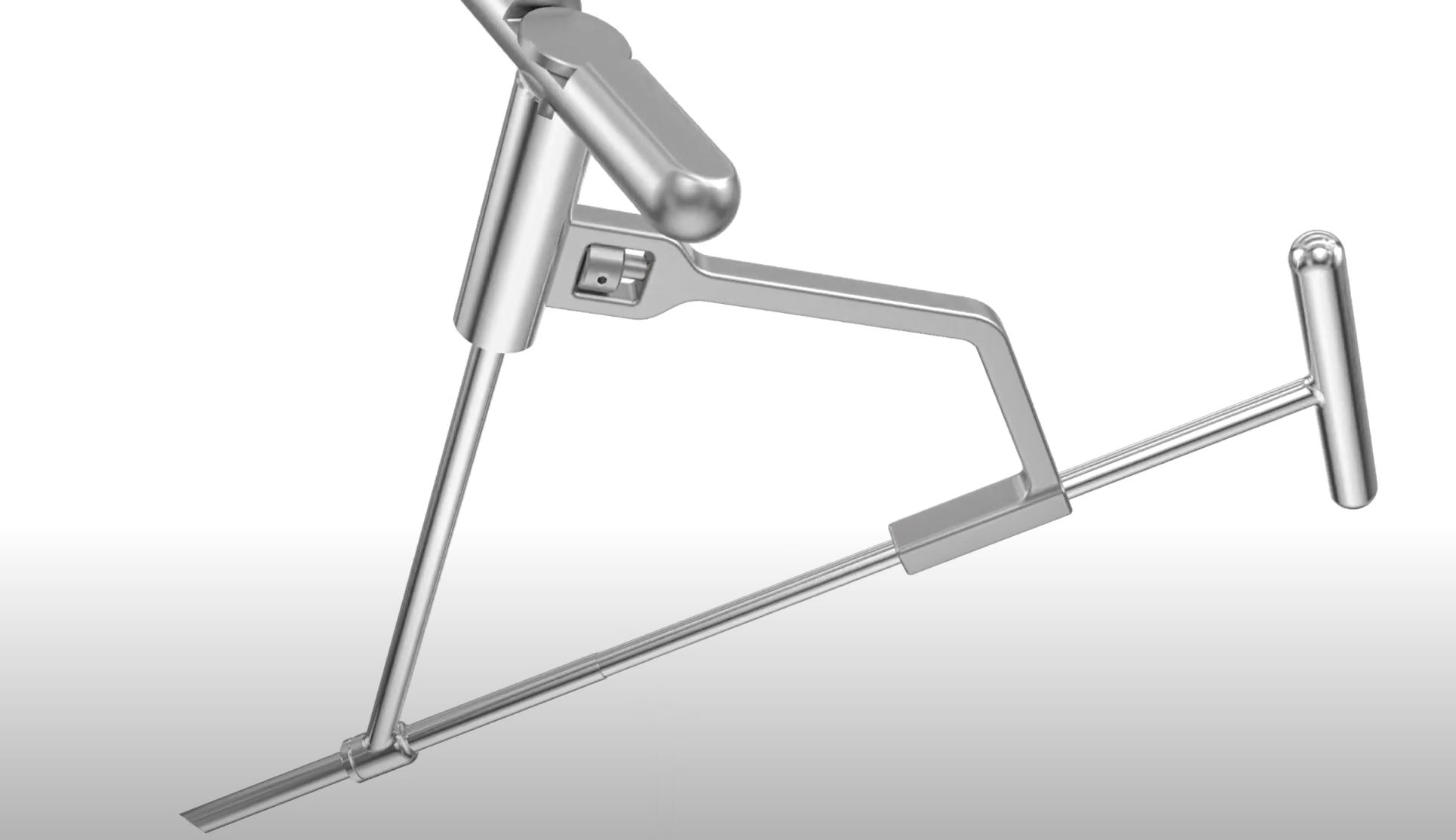
Anterior Path® approach for total hip arthroplasty
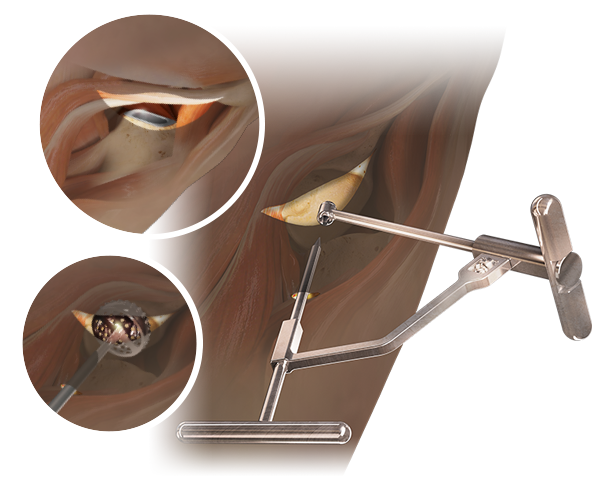
Anterior Path® is an anterior, portal-assisted approach for hip replacement that utilizes a cannula to gain direct access to the acetabulum, offering direct visualization and in-line preparation of the acetabulum and femur. The use of the cannula allows for a transverse incision to be made more superior and lateral, minimizing many challenges related to the femur and wound healing.
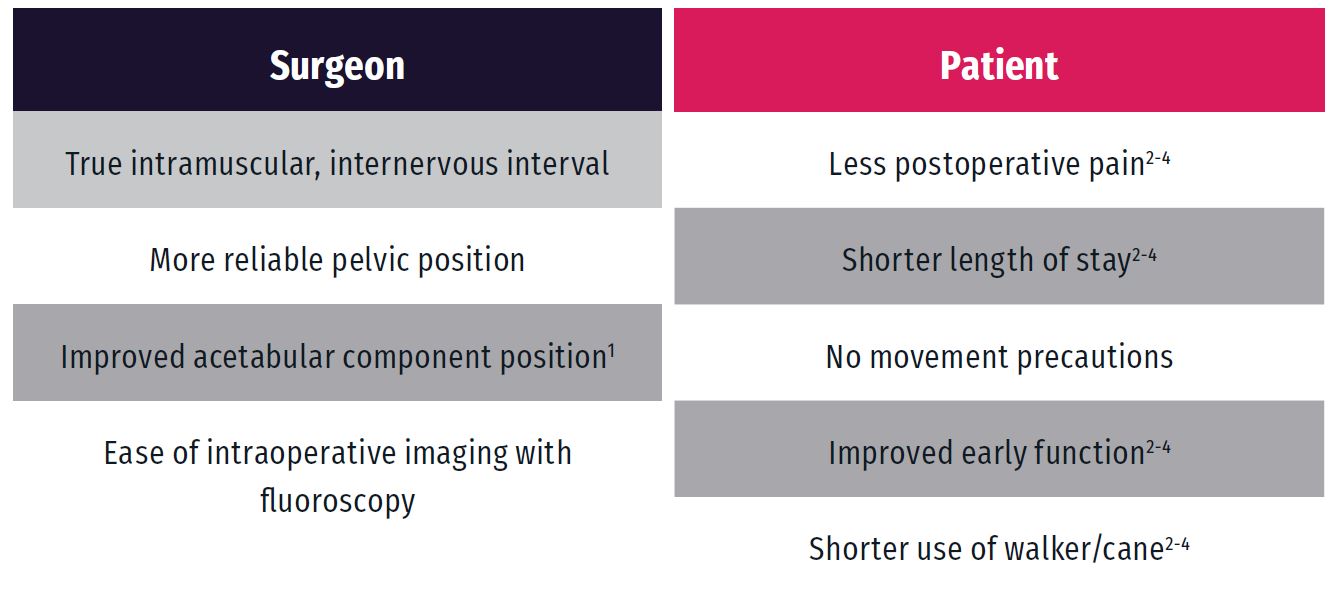
Advantages of the Direct Anterior(DA) approach
Direct anterior approach matches outcomes with modern surgeon and patient demands
But, there are challenges...
The Direct Anterior Approach for total hip arthroplasty (THA) is effective; however, it still provides many challenges for physicians.
- Steep learning curve—increased operative time, increased blood loss, higher complication rate5
- Creating access to the femur is challenging, leading to femoral complications such as periprosthetic fracture6
- Increased rate of wound complications7
- Limitations in choice of femoral stem type
AND CHALLENGES HAVE LED TO COMPROMISES
Because of some of the challenges associated with the Direct Anterior approach, compromises must be made to achieve adequate femoral visualization & accurate, reproducible component placement.
- Additional assistants and technology
• Intra-operative fluoroscopy
• Specialized operative tables
• Offset instrumentation
• Extensive soft tissue releases
• New short femoral stems
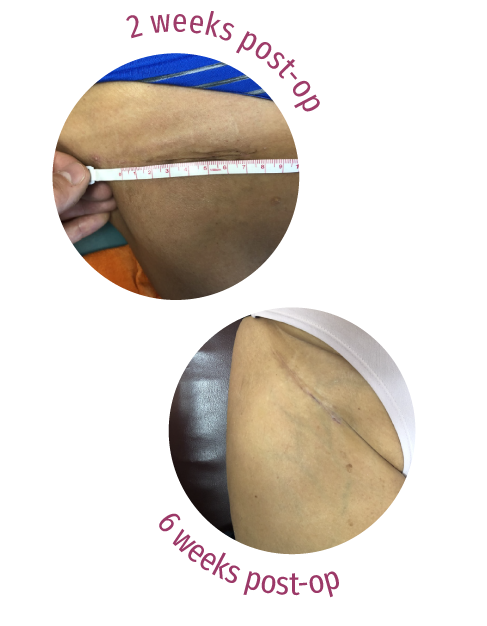
DIRECT ANTERIOR WOUND COMPLICATIONS
The incidence of wound complications is 7 times higher with the use of the Direct Anterior approach, and does not improve with surgeon experience.8 Utilizing a Direct Anterior approach Skin incision is not in line with Langer’s lines, which correspond to the natural orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis Wound is under constant tension Poor wound perfusion
ANTERIOR® PATH INCISION BENEFITS
The Anterior Path® incision is made in line with Langer’s lines and just below the hip crease, providing a number of benefits9:
- Improved Wound Cosmesis
- Improved Wound Healing10
- Fewer Wound Complications
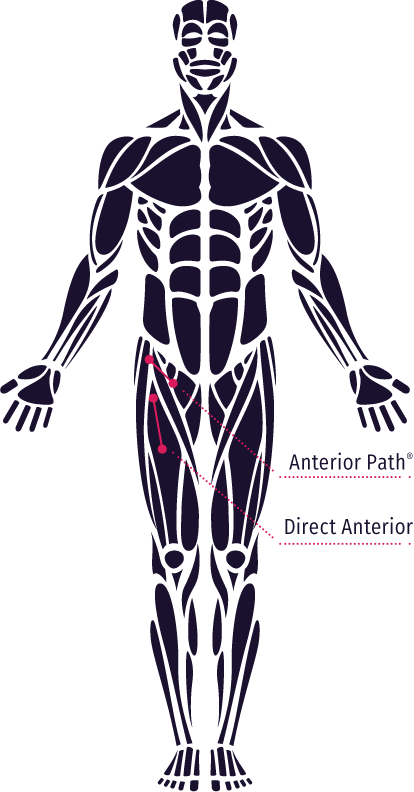
ANTERIOR PATH® & THE LATERAL FEMORAL CUTANEOUS NERVE
Retraction required by the Direct Anterior approach to gain access to the hip has led to injury of the LFCN, which results in tingling, numbness and burning pain in the patient’s thigh. Due to the change in the location and orientation of the incision in Anterior Path®, the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN) is more easily avoided. A study on DA showed that a transverse incision reduced subsequent anterior thigh numbness by nearly half.9
- A comparative study of Direct Anterior shows that in 964 patients there was approximately 1.9 times as much numbness with a longitudinal incision versus a bikini incision.9
PRECAUTIONS & DISCLAIMERS
Every patient is different, and individual results will vary. There are risks and recovery times associated with surgery.
These surgeons are paid consultants for MicroPort Orthopedics. The opinions expressed are theirs alone and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of MicroPort Orthopedics Inc.
-
References
- As compared to posterior approach THA. Grammatopoulos G et al. Bone Joint J. 2018 Oct;100-B(10):1280-1288.
- As compared to posterior approach THA. W P Barrett et al./ J of Arthroplasty 28 (2013) 1634-1638.
- As compared to posterior approach THA. M J Taunton et al. / J Arthroplasty 29 Suppl. 2 (2014) 169-172.
- As compared to posterior approach THA. Taunton MJ et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018.
- Spaans AJ, van den Hout JA, Bolder SB. High complication rate in the early experience of minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty by the direct anterior approach. Acta Orthop 2012;83:342-6.
- Hartford JM, Knowles SB. Risk Factors for Perioperative Femoral Fractures: Cementless Femoral Implants and the Direct Anterior Approach Using a Fracture Table. J Arthroplasty 2016;31:2013-8
- Christensen CP, Karthikeyan T, Jacobs CA. Greater prevalence of wound complications requiring reoperation with direct anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2014;29:1839-41
- Christensen CP, Jacobs CA. Comparison of Patient Function during the First Six Weeks after Direct Anterior or Posterior Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA): A Randomized Study. J Arthroplasty 2015;30:94–97
- Leunig et al. Skin crease ‘bikini’ incision for the direct anterior approach in total hip arthroplasty. The Bone & Joint Journal Vol. 100-B, No. 7. 28 Jun 2018
- Statistically significant for obese patients. Manrique J, Paskey T, Tarabichi M, Restrepo C, Foltz C, Hozack WJ. Total Hip Arthroplasty Through the Direct Anterior Approach Using a Bikini Incision Can Be Safely Performed in Obese Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2019 Aug;34(8):1723-1730



